Semantic Search: What it is & How to Use it for SEO?
Search engines have come a long way from simply matching keywords to delivering highly relevant, intent-driven results. In 2025, semantic search is not just a trend—it’s the backbone of how search engines like Google understand and serve content.
As algorithms grow increasingly sophisticated, traditional SEO tactics that focus solely on keywords are no longer enough. This is where semantic search comes—a game-changing approach that prioritizes meaning, context, and user intent.
Whether you’re an SEO professional, a content marketer, or a business owner looking to boost your digital presence, understanding semantic search is critical to staying ahead in the ever-evolving world of search engine optimization.
In this blog, we’ll break down what semantic search really means, why it matters, and—most importantly—how you can harness its power to improve your SEO strategy, drive more traffic, and achieve higher rankings in search results.
What is Semantic Search?
At its heart, Semantic Search is a data searching technique used by search engines to understand the contextual meaning and intent behind a user’s search query, rather than just matching the literal keywords entered.
Think about it: when you search for something, you’re usually looking for an answer, a solution, or information about a concept, not just pages containing specific words. Semantic search aims to bridge the gap between the user’s intention and the information available online.
Traditional vs. Semantic Search
- Traditional Search: Focused primarily on matching keywords in a query to keywords on a webpage. This often led to irrelevant results if the exact phrasing wasn’t used or if words had multiple meanings.
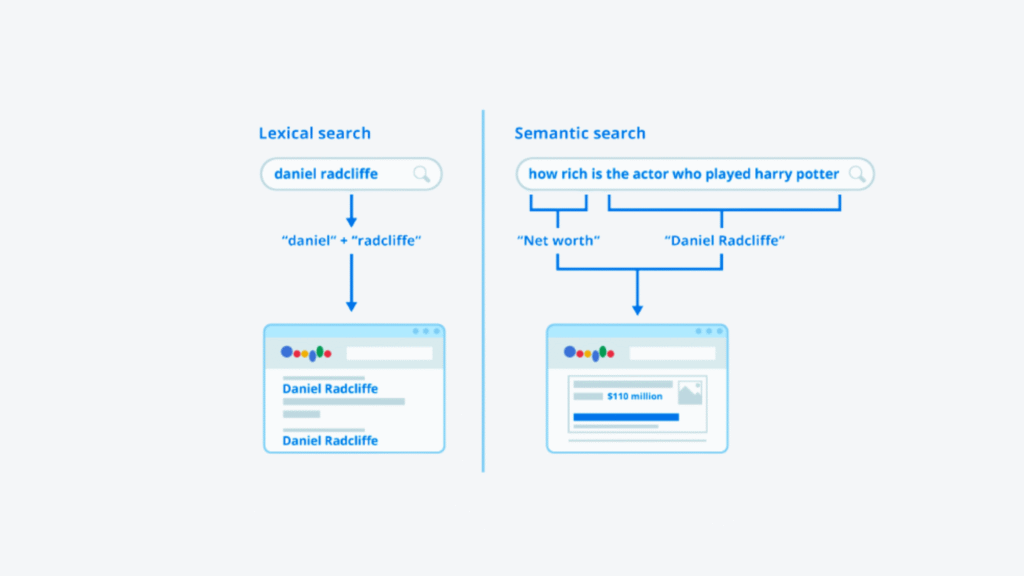
- Semantic Search: Focuses on understanding:
- User Intent: What is the user trying to achieve with this search? (e.g., learn, buy, find a location).
- Context: What is the broader context of the query? This includes location, search history, time of day, and the overall topic.
- Relationships Between Words & Concepts: How do the words in the query relate to each other and broader concepts and entities?
The Role of AI and Algorithms:
Google’s journey towards semantic understanding took a major leap with the Hummingbird update in 2013, which focused on understanding the meaning behind queries, especially conversational ones. Since then, advanced AI and machine learning models have become central:
- RankBrain: Google’s AI system that helps interpret queries, especially novel ones, to find pages that might not have the exact keywords but match the underlying intent.
- BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers): Allows Google to understand the nuances and context of words in searches by processing the entire sentence bidirectionally (looking at words before and after a term). BERT significantly improves understanding of prepositions and complex queries. Google has stated that BERT impacts a significant portion of search queries.
- MUM (Multitask Unified Model): Even more powerful than BERT, MUM is designed to understand information across different languages and formats (text, images, video) simultaneously. It aims to answer complex questions that don’t have simple answers.
These technologies allow search engines to function less like simple databases and more like intelligent assistants, deciphering the why behind the what.
How Does Semantic Search Actually Work?
Semantic search relies on several interconnected technologies to understand language and deliver relevant results:
1. Natural Language Processing (NLP)
A field of AI focused on enabling computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language.1 NLP techniques help search engines break down query structure, identify parts of speech, understand sentiment, and grasp the overall meaning.
2. Entity Recognition
Search engines identify and understand real-world objects or concepts called “entities” – people, places, organizations, products, ideas (e.g., “Apple” the company vs. “apple” the fruit). They analyze content to spot these entities and understand how they relate.
3. Knowledge Graphs
These are vast databases of interconnected entities and their relationships. Google’s Knowledge Graph, for example, stores billions of facts about people, places, and things, allowing it to provide direct answers (like in knowledge panels) and understand the connections between concepts mentioned in a query and on a webpage.
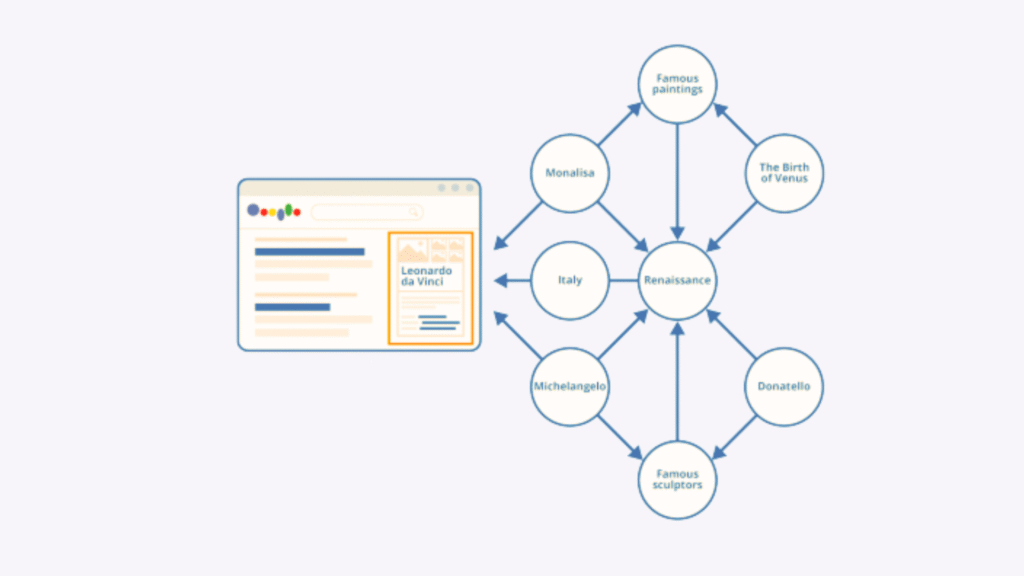
4. Contextual Understanding
Algorithms analyze various signals – the specific words used, synonyms, related concepts, user location, past searches, time of day, and the overall topic of the query – to determine the most likely search intent and provide tailored results.
5. Vector Embeddings
A more recent advancement is where words, phrases, and even entire documents are represented as mathematical vectors in a multi-dimensional space. Items with similar meanings are located closer together in this space. This allows search engines to find relevant content even if it doesn’t use the exact keywords, simply by finding content vectors close to the query vector.
Why Semantic Search is Important for SEO in 2025?
Ignoring semantic search means falling behind. Here’s why embracing a semantic approach is critical:
1. Improved Search Relevance & User Experience
The primary goal of search engines is user satisfaction. Semantic search delivers more accurate, relevant results that directly address user intent. Websites providing this value are rewarded with better visibility. Satisfied users stay longer, engage more, and are less likely to bounce back to the search results – all positive signals for SEO.
2. Moving Beyond Outdated Tactics
Keyword stuffing and focusing solely on exact-match keywords are ineffective and can even lead to penalties (think historical updates like Panda and Penguin targeting low-quality content). Semantic SEO focuses on quality, relevance, and comprehensiveness.
3. Ranking for Broader Concepts
Content optimized for topics and intent naturally ranks for a wider array of related searches, including long-tail keywords (longer, more specific phrases). Statistics show that around 87% of searches are long-tail, indicating users seek detailed answers (according to Ahrefs data, mentioned by HeadsOnPillows).
4. Building Topical Authority & Trust (E-E-A-T)
Creating comprehensive, interconnected content around specific topics demonstrates your Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness (E-E-A-T). Search engines prioritize content from sources they deem authoritative on a subject. Topic clusters, a core semantic SEO strategy, directly support building this authority.
5. Enhanced Visibility through Rich Results
Semantic understanding, especially when aided by structured data, allows search engines to generate rich results (like featured snippets, FAQs, knowledge panels).
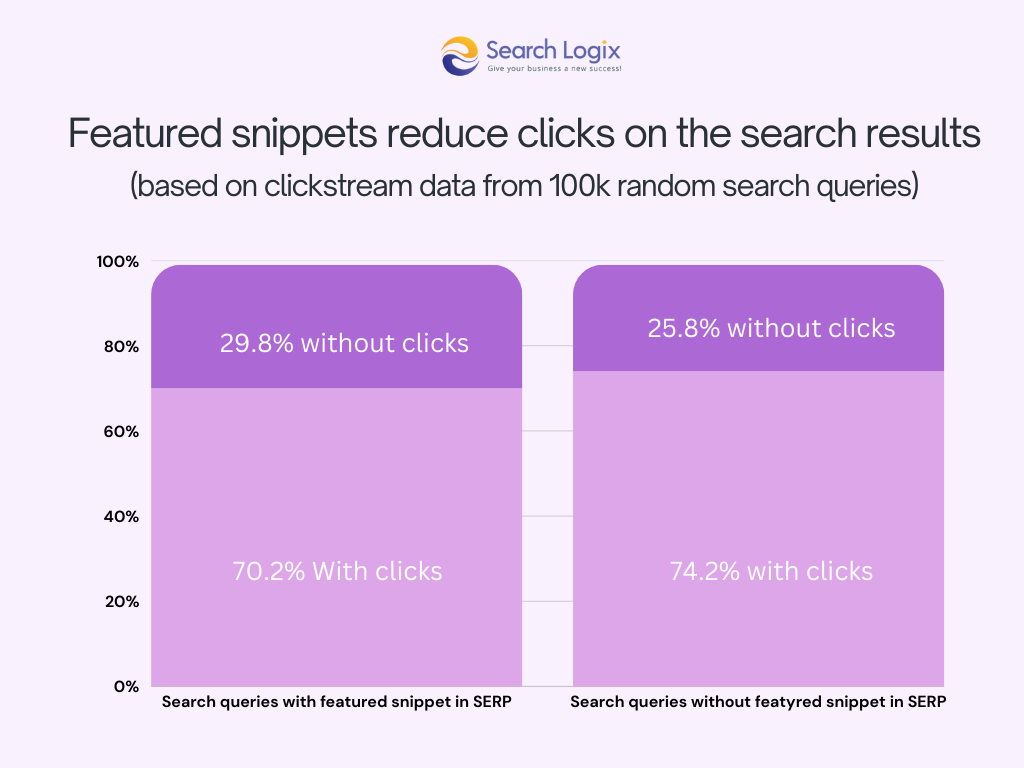
Studies suggest sites using structured data are significantly more likely (e.g., 4x according to Moz data cited by Tekrevol) to appear in these prominent SERP features, boosting visibility and click-through rates.
6. Future-Proofing Your Strategy
As AI continues to evolve (with models like MUM and beyond), search engines will only get better at understanding meaning. Aligning your SEO strategy with semantic principles makes it more resilient and adaptable to future algorithm updates.
How to Optimize Your Content for Semantic SEO?
Transitioning to a semantic SEO approach involves shifting your focus from keywords alone to topics, intent, and context. Here’s how:
1. Deeply Understand and Target User Intent
Before writing a single word, figure out why someone is searching for your target topics. There are four main types of search intent:
- Informational: Seeking information (e.g., “how does semantic search work?”)
- Navigational: Looking for a specific website or brand (e.g., “Google Search Console login”)
- Transactional: Intending to make a purchase or take a specific action (e.g., “buy SEO software”)
- Commercial Investigation: Comparing products or services before purchase (e.g., “best SEO tools 2025”)
How to Optimize:
- Analyze the SERPs: Search for your target topics and see what kind of content ranks (blog posts, product pages, guides, lists?). This reveals the dominant intent Google recognizes.
- Check “People Also Ask” & “Related Searches”: These sections show related questions and queries, offering direct insight into user intent and related subtopics.
- Tailor Content: Create content formats that match the intent (e.g., blog posts for informational, product pages for transactional). Use appropriate calls-to-action (CTAs).
2. Build Topic Clusters (Hub-and-Spoke Model)
Organize your content strategically to demonstrate topical depth and authority.
- Pillar Page: A comprehensive page covering a broad core topic (the “hub”).
- Cluster Content: Multiple pages delving into specific subtopics related to the pillar (the “spokes”).
How to Optimize:
- Identify Core Topics: What main subjects are central to your business and audience?
- Map Subtopics: Brainstorm or research specific questions, angles, and related concepts for each core topic. Keyword research tools can help here.
- Create Content: Develop in-depth content for the pillar page and detailed content for each cluster page.
- Interlink Strategically: Link cluster pages back to the pillar page, and link relevant cluster pages to each other using descriptive anchor text. This helps search engines and users navigate related information and understand the structure.
3. Write Naturally, Comprehensively, and Answer Questions
Focus on creating high-quality, valuable content that truly addresses the user’s needs.
How to Optimize:
- Natural Language: Write for humans, not bots. Use conversational language and structure content logically. Avoid keyword stuffing.
- Comprehensiveness: Cover topics thoroughly. Answer common questions related to the subject within your content. Aim to be the best resource available for that specific topic or subtopic.
- Incorporate Related Terms: Naturally weave in synonyms, variations, and semantically related keywords (sometimes called LSI keywords). For example, if writing about “coffee brewing,” include terms like “pour-over,” “espresso machine,” “grind size,” “water temperature,” etc. Tools like Google Autocomplete, Related Searches, and SEO platforms can help find these terms.
4. Leverage Structured Data (Schema Markup)
Give search engines explicit context about your content. Schema markup is code added to your website that labels specific content elements (like FAQs, recipes, products, articles, events).
How to Optimize:
- Identify Opportunities: Determine which schema types are relevant to your content. Common types include Article, FAQ Page, How-To, Product, Local Business, Event.
- Implement Correctly: Use tools or plugins to generate and add schema markup (JSON-LD is the preferred format).
- Test Your Markup: Use Google’s Rich Results Test tool to ensure your schema is implemented correctly and eligible for rich results.
5. Optimize for Entities
Entities help search engines recognize and understand the key people, places, things, and concepts mentioned in your content.
How to Optimize:
- Be Clear: Define entities clearly within your text.
- Provide Context: Ensure the surrounding text clarifies the meaning and relationship of entities.
- Link Appropriately: Link entity names to authoritative sources (like Wikipedia or official websites) where relevant, especially for less common entities.
6. Enhance Internal Linking
Go beyond just topic clusters; ensure logical linking across your entire site where relevant.
How to Optimize:
- Connect Related Content: Link blog posts, service pages, and product pages where it makes sense and adds value for the user.
- Use Descriptive Anchor Text: Use anchor text that accurately describes the content of the linked page, incorporating relevant keywords naturally.
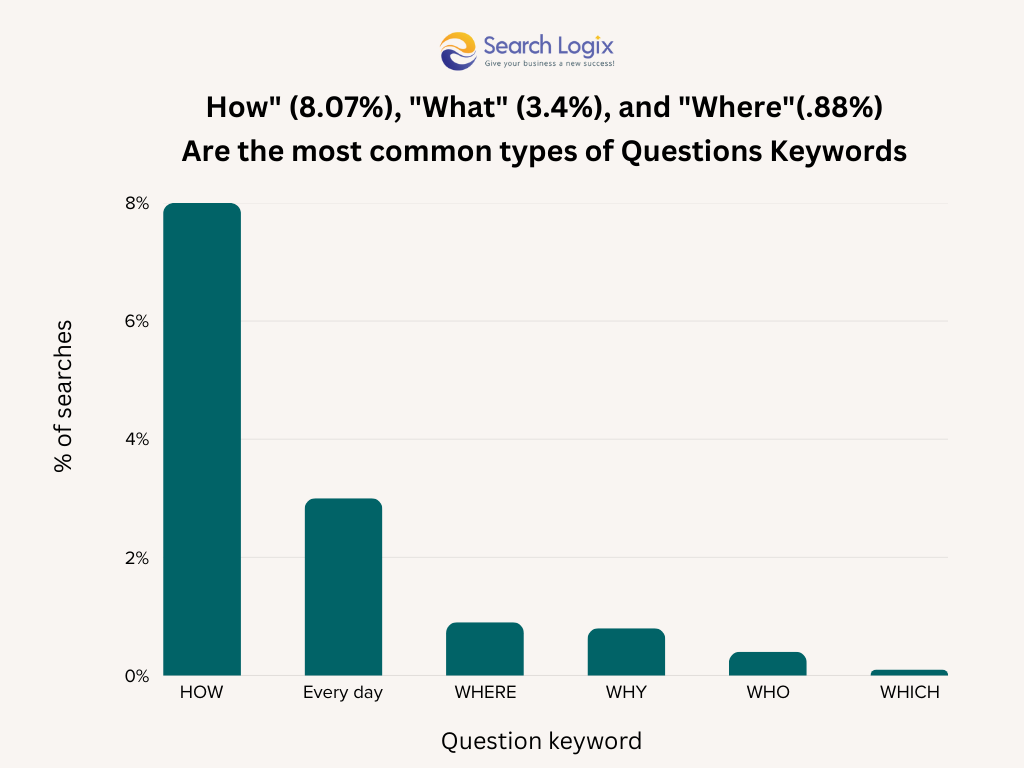
7. Optimize for Voice Search & Questions
Voice search queries are often longer and phrased as natural questions. Moreover, voice search optimization is already in the top SEO trends.
How to Optimize:
- Target Question Keywords: Use tools like AnswerThePublic or analyze “People Also Ask” to find common questions.
- Provide Direct Answers: Structure content to answer these questions clearly and concisely, often near the beginning of a relevant section. FAQ pages with schema are great for this.
8. Update and Refresh Existing Content
Semantic SEO isn’t just about new content. Regularly review and update older posts.
How to Optimize:
- Identify Underperforming Content: Find posts that could benefit from optimization.
- Enhance with Semantic Keywords: Add related terms and concepts naturally.
- Update Information: Ensure facts, statistics, and advice are current.
- Improve Structure & Readability: Refine formatting for a better user experience.
The Future is Semantic: What’s Next?
Semantic search has fundamentally changed SEO. It requires a shift from a narrow focus on keywords to a broader strategy centered on understanding user intent, providing comprehensive value, and structuring content logically.
Semantic search is not a destination but an ongoing journey. Here’s what to expect:
1. Deeper AI Understanding
AI models like Google’s MUM (and future iterations) will become even better at understanding complex information across different formats and languages, making semantic relevance paramount.
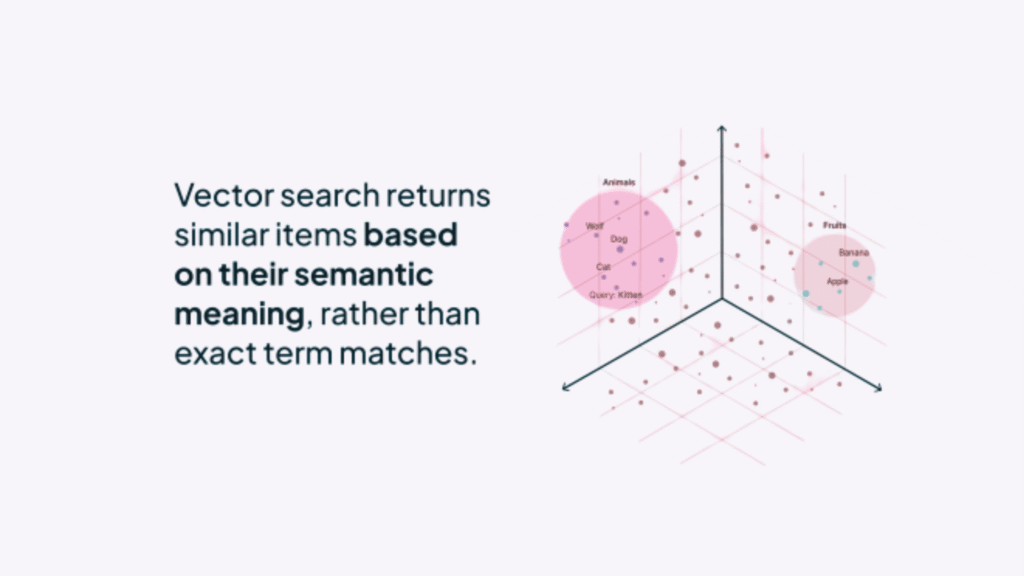
2. Rise of Vector Search
The shift towards vector embeddings means that optimizing for meaning and relationships will become even more central than optimizing for specific keyword strings.
3. AI Overviews & Generative AI
Features like Google’s AI Overviews generate direct summaries based on semantic understanding, making it crucial for your content to be clear, well-structured, and authoritative to be included or referenced.
4. Increased Personalization
Search results will likely become even more personalized based on individual user context and history, reinforcing the need to understand diverse user intents.
Partner with a Top SEO Company like eSearch Logix to Leverage Semantic SEO
Implementing semantic SEO effectively requires more than just understanding keywords—it demands a deep grasp of search intent, content architecture, NLP-driven strategies, and continuous adaptation to algorithm updates.
That’s where partnering with a specialized SEO agency like eSearch Logix makes all the difference. As a leading SEO company with a proven track record, we blend advanced technical expertise with content intelligence to help businesses unlock the full potential of semantic search.
Whether you’re a startup, enterprise, or eCommerce brand, their team offers tailored solutions that align with how search engines—and users—think today.
Why Choose eSearch Logix?
- Expertise in Semantic SEO & NLP: Stay ahead with strategies based on real-time data and algorithm behavior.
- Custom Content & Topic Clusters: Build authority through well-structured content ecosystems that satisfy user intent.
- Structured Data Implementation: Improve visibility in rich snippets and featured results with expert schema markup.
- Data-Driven Insights: Gain actionable intelligence through detailed SEO audits, user behavior tracking, and competitor analysis.
- Voice & Conversational Search Optimization: Position your brand for the future of search with voice-first strategies.
Search is no longer just about matching words—it’s about matching meaning. If you’re ready to scale your visibility, traffic, and conversions through smarter, intent-driven SEO, eSearch Logix can be the strategic partner you need.
Contact us today to discover how semantic SEO can transform your digital growth.







