In recent years, CDN technology gained popularity. Companies always look for ways to reduce latency, deliver better performance, and reduce costs. It is right for businesses looking to serve large amounts of heavy content, such as video streaming, gaming, and software downloads.
The content Delivery Network (CDN) Security market is estimated to reach $8.85 billion by 2025. The global CDN market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate CAGR of 26.2% from 2020 to 2025. Increasing demand for content delivery services driving the growth. Growing use of CDN technology for web and mobile applications with the adoption of cloud-based services is visible.
Table of content:
- What is a CDN?
- Why is a CDN important?
- What are the benefits of CDNs?
- What is the history of CDN technology?
- What internet content can a CDN deliver?
- How does a CDN work?
- What are the applications of CDN?
- What is a CDN?
Content Delivery Networks are networks of servers that deliver content to end users. They increase the performance and availability of web content.
Content delivery networks, or CDNs, are a network of servers that deliver content to end users. It increases the performance and availability of web content by delivering it from the server closest to the user’s location. It does not work from a single centralized server in one location.
Why is a CDN important?
A CDN can improve the speed at which webpages load for end users by storing copies of data close to them.
A CDN is important for a business because it can help with the online brand image of your company. For example, if you are an e-commerce store and you deliver your products from your location instead of utilizing a CDN service. Then your site may load late, and customers may not want to buy from you because they know that there are other sites out there with faster loading times.
CDNs help to ensure website loads faster and have more uptime. It helps businesses in digital marketing by improving online performance and increasing customer satisfaction.
What are the benefits of CDNs?
CDNs are becoming more popular in several niches including digital marketing as well. Because, they can provide faster and more reliable website loading speeds for customers. The main benefit of using a CDN is, it reduces server load, which can increase website performance by enhancing content availability.

CDNs are a type of content delivery network that help with the load on your website by distributing static content to servers all around the world. This way, when a user accesses your site, they will have reduced loading time because the content is being delivered from a server that is close to them.
- Decrease Server Load: CDN runs over the cloud, so all the graphic and content load is easy to handle with CDN. It reduces the load on service to improve website loading speed.
- Improve Site Speed and Website Performance: decreased server load and flexible storage access enhance the website performance in aspect of content representation.
- Allow Audience Segmentation Based on User Analytics: CDN providers could use metrics such as page views, time spent on the page, and bounce rate to identify patterns in user engagement.
- Enable Advanced Website Security: Cloud accounts are always encrypted and protected with a user id and password. So your content and graphics are always in safe hands.
- Enhance Content Availability: Fast speed and cloud reliability allow the users to access any content anywhere from remote servers.
- Contribute to Cost Savings by Reducing Bandwidth: Reduced bandwidth and fewer requirements to reduce the cost of the process.
What is the history of CDN technology?
The history of Content Delivery Network (CDN) technology traces back to the mid-1990s, when the first CDN was created to address the increasing demand for content delivery over the Internet.
The primary purpose of a CDN was to improve the performance of web-based applications by distributing static content and streaming media to many geographic locations. With the emergence of new technologies like broadband, mobile, and cloud computing, CDN technology expanded to include more sophisticated services such as application delivery, dynamic web content, and cloud storage.
As the demand for content delivery over the Internet increased. CDNs increased in popularity and businesses began to use it to deliver content for websites and applications.
Today, CDNs are used by millions of websites and applications to deliver content to their users. CDNs have become an essential component of the web infrastructure and have enabled faster and more reliable content delivery. CDNs are also used to provide website security such as DDoS protection and to optimize website performance for users around the world.
What digital content can a CDN deliver?
CDN servers around the world can deliver a variety of content types, including web pages, streaming media, software downloads, images, and videos. CDNs use a variety of technologies to improve the delivery of web content, including caching, load balancing, and content optimization.
CDNs are often used to improve the speed and availability of web content. CDNs can deliver a variety of web content, including static content such as HTML pages, JavaScript, and CSS files. Dynamic content such as database queries and API calls; streaming media such as audio and video, and software downloads.
CDNs can also deliver large files such as images and videos, as well as content that needs protection, such as e-commerce payment pages and confidential information.
CDNs can also provide security by protecting websites from malicious attacks, such as DDoS attacks, and by minimizing the risk of data breaches. CDNs can also improve website performance by reducing latency and improving website responsiveness.
How does a CDN work?
A web server handles serving content to end users. Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) are a series of distributed servers that are present in various geographical locations. Let’s get to understand the stepwise process of CDN.
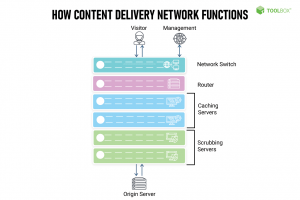
Source: Spiceworks
- When a user requests content from a web server, the CDN redirects the request to the closest server.
- This server then delivers the content to the user, providing faster access than if the request had to travel to the original server.
- The CDN also helps ensure that the content is delivered and, as the user’s request is routed to the server that is closest to them.
The CDN also provides more features such as caching, load balancing, and security. By using a CDN, content can be delivered to users, regardless of where they are located.
What is a CDN used for?
CDN is introducing advanced-level benefits and applications into different industries across the globe.
- Content Delivery: CDNs are used to deliver content such as images, videos, and webpages to users in an efficient and timely fashion. They can store static content in many locations to reduce latency and optimize the user experience.
- Security: CDNs offer many security benefits such as DDOS protection, malware scanning, and encryption of data.
- Scalability: CDNs are used to scale content delivery for websites and applications that are experiencing high levels of traffic.
- Cost Savings: CDNs can help to reduce the costs of content delivery by offloading traffic from the origin servers.
- Video Streaming: CDNs are used to stream large amounts of video content to users. This is done by using many servers and caching data in many locations.
- Real-time Applications: CDNs are used to deliver real-time applications such as video chat, online gaming, and VoIP.
Many businesses are turning to CDN solutions to help manage their content delivery needs. This is because CDNs can offload traffic from origin servers and decrease latency, as well as improve content availability and scalability.
Conclusion
Trends in the CDN industry include the use of artificial intelligence to improve performance, the adoption of edge computing, and the increasing use of 5G technology. As CDN solutions become more advanced and more adopted, the global CDN market is expected to continue to grow. Reach out the expert consultants for cloud services. Get help with the CDN implementation of your business model.

